RAP Database Tables
Published: November 2025
| Topic | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Database Key (RAP) | The technical primary key of the underlying DDIC table used by a RAP BO’s CDS view entity. |
| Role in RAP | Instance identification, locking, drafts, transactions, update operations. |
| Semantic Key | A business-meaningful key, different from the technical DB key. |
| Table Without Key? | Allowed in ABAP Dictionary, but not allowed in RAP, and generally bad practice. |
How to Create RAP Database Tables Through Eclipse
To create a database table, right-click on Database Table under Dictionary in the Project Explorer. Alternatively, click on the menu File → New → Other. Search for Database Table and press Enter.
Provide the name and description, then click Next. Select a Transport Request if available and click Finish.
Once the creation is completed, a new database table should be generated as follows:
@EndUserText.label : 'Student Academic Result'
@AbapCatalog.enhancement.category : #NOT_EXTENSIBLE
@AbapCatalog.tableCategory : #TRANSPARENT
@AbapCatalog.deliveryClass : #A
@AbapCatalog.dataMaintenance : #RESTRICTED
define table zstudent_ar_m_bd {
key client : abap.clnt not null;
}
Complete form of table declaration might look as follow:
@EndUserText.label : 'Student Details'
@AbapCatalog.enhancement.category : #NOT_EXTENSIBLE
@AbapCatalog.tableCategory : #TRANSPARENT
@AbapCatalog.deliveryClass : #A
@AbapCatalog.dataMaintenance : #RESTRICTED
define table zstudent_m_bd {
key client : abap.clnt not null;
key id : sysuuid_x16 not null;
firstname : abap.char(100);
lastname : abap.char(100);
age : abap.numc(3);
course : abap.char(50);
courseduration : abap.numc(4);
status : abap_boolean;
gender : abap.char(1);
dob : abap.dats;
lastchangedat : abp_locinst_lastchange_tstmpl;
locallastchangedat : abp_lastchange_tstmpl;
}
Primary Key
In RAP, the database key refers to the primary key of the underlying database table used by the CDS root view entity of a RAP BO (Business Object).
🔍 How RAP Uses the Database Key
-
a) To identify unique instances
Every RAP operation—create, update, delete, read—is anchored around the key fields.
-
b) For lock management
RAP generates lock objects implicitly based on the key.
-
c) For deep transactions
Keys allow RAP to perform hierarchical operations (root → child → subchild).
-
d) For etags & optimistic locking
Keys enable RAP to control versioning and concurrency.
-
e) During draft handling
Draft keys are partly derived from the database key of the active entity.
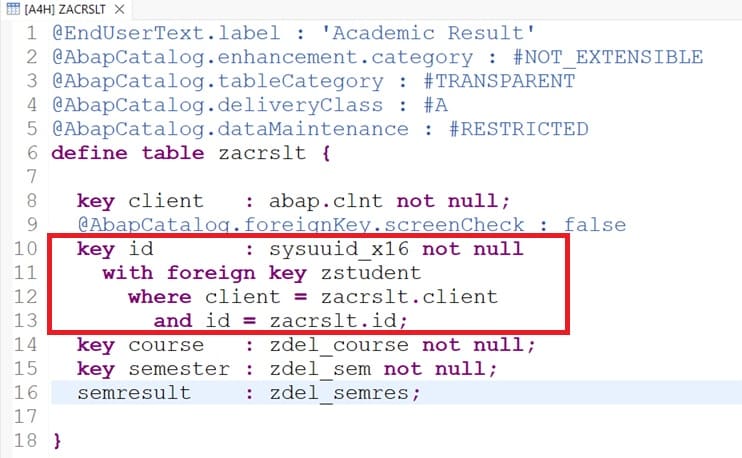
Foreign Key
Foreign key concept is also applicable in RAP. Creating the table with foreign key in SAP is shown as below:
@EndUserText.label : 'Academic Result'
@AbapCatalog.enhancement.category : #NOT_EXTENSIBLE
@AbapCatalog.tableCategory : #TRANSPARENT
@AbapCatalog.deliveryClass : #A
@AbapCatalog.dataMaintenance : #RESTRICTED
define table zacrslt {
key client : abap.clnt not null;
@AbapCatalog.foreignKey.screenCheck : false
key id : sysuuid_x16 not null
with foreign key zstudent
where client = zacrslt.client
and id = zacrslt.id;
key course : zdel_course not null;
key semester : zdel_sem not null;
semresult : zdel_semres;
}
Data type
Data Type